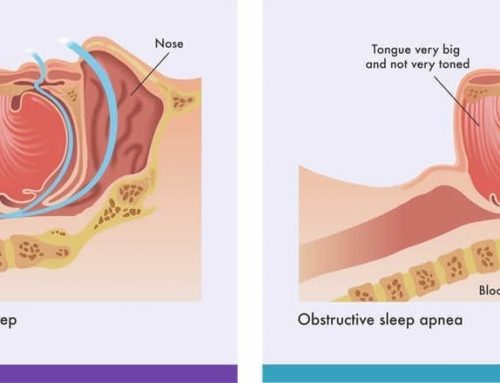
Do You Need to be Concerned About the Health Effects Of Sleep Deprivation?
24 ways sleep deprivation affects health
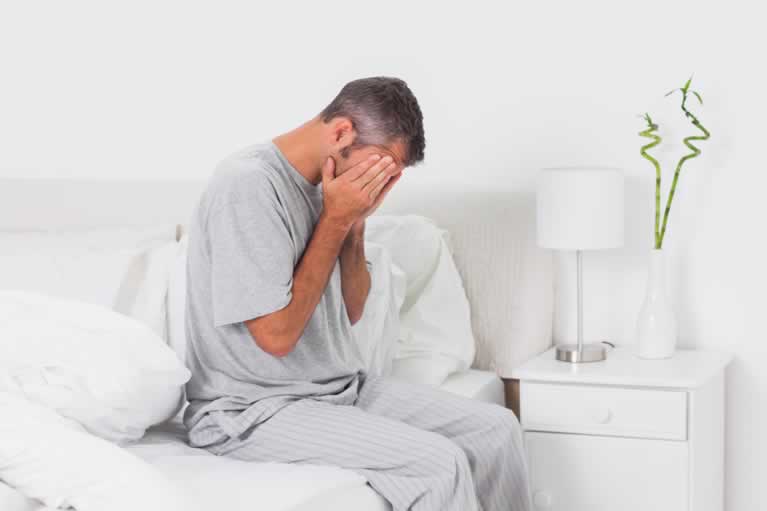
Not getting enough sleep regularly means more than morning crankiness. You need sleep as much as you need to breathe and eat. While you’re sleeping, your body is busy tending to your physical and mental health and getting you ready for another day.
When you’re sleep deprived, your body does not get the chance to rejuvenate, affecting the how your brain functions, cognitive abilities, and emotional state. When sleep deprivation becomes chronic, it can interfere with balance, coordination, and even decision-making.
Here are 24 other major health effects caused by sleep deprivation:
Alertness
Have you ever noticed, when you’re sleepy, you don’t always pay the closest attention to things? That’s because you are focused on staying awake, rather than staying alert. Even missing out on as little as 1.5 hours of sleep can reduce daytime alertness by up to 32%.
Anxiety
Lack of sleep can intensify the brain’s anticipatory responses to daily events. This can cause anxiety and constant worry through the day.
Bones
Researchers found changes in bone remodeling, which controls the repair, strength, flexibility, and density of your bones, and bone marrow development due to chronic sleep deprivation. This can result in osteoporosis and problems healing fractures and microdamage caused by daily activities.
Brain Activity
Your brain needs plenty of rest in order to clean itself. Spinal fluid is pumped more quickly throughout the brain clearing away all the waste created by brain cells, leaving you refreshed and alert in the morning. Shortened or interrupted sleep results in that groggy, bogged down, and distracted state of mind.
Cancer
According to the National Sleep Foundation, studies have shown that lack of sleep can increase the risk of cancer. In fact, going to bed too late can double the risk of breast cancer because of late night exposure to light, which is linked to reduced melatonin production. Reduced melatonin production disrupts estrogen levels, and too much estrogen is known to promote breast cancer.
According to a study in the International Journal of Cancer, the rate of breast cancer in women was found to be 30% higher for those who had worked shifts – working irregular hours. Women who had over four years of night shift work were at even higher risk.
Circadian Rhythm
Our bodies have a natural time clock, known as our circadian rhythm, which regulates our sleep-wake cycle. Circadian rhythms are disrupted when one does not have a regular sleep schedule that aligns with our natural clock. Disruptions in circadian rhythms can lead to poor white blood cell health.
Cognition
Sleep deprivation affects cognition on multiple levels. On a primary level, it impairs your attention and alertness. It also impairs your creativity, reaction time, and problem-solving skills. Finally, it makes it difficult to control your emotions, delivering negative impacts to your mood, perception and memory, frustration tolerance, and ability to use emotions to inform your decision making.
A number of studies have shown that many of these impacts remain even after a stimulant like caffeine restores alertness and attention. Mounting evidence also suggests that the impact on cognitive systems that rely on emotional data may be greatest.
Death
Insufficient sleep can significantly raise your risk of accidental death from any cause. This could be anything from drowsy driving or even just walking across the street without paying attention. When you’re sleep deprived, you’re not fully aware of your surroundings, and anything can happen. In fact, you are 20% more likely to die within 20 years if you are currently suffering from sleep deprivation. Even more so, sleeping fewer than 5 hours each night can increase this risk by up to 26%.
Depression
Lack of sleep can have a significant impact on your mental state. People who have insomnia are five times more likely to develop signs of depression than those without. This is because inadequate sleep causes a decrease in neurotransmitters that regulate mood. Poor sleep can also intensify the effects of depression and other mental health disorders creating a cycle of losing sleep and falling into a deep depressive state.
Diabetes
Insulin is a hormone that regulates blood sugar in your bloodstream. Not receiving the right amount of sleep your body needs reduces the release of insulin, contributing to type 2 diabetes. In response to lack of insulin, your body secretes the stress hormones cortisol and norepinephrine, which make it even harder for insulin to effectively regulate blood sugar and gives you a higher risk of developing diabetes.
DNA
A study showed that just one week of insufficient sleep could alter the activity of our genes, which control our response to stress, immunity, inflammation and overall health. Sleep deprivation alters the function of over 700 of our genes – including those that affect stress response, immune system, and metabolism.
Hallucinations
If you go long enough without sleep, you may begin to hallucinate. Sleep deprivation is known to impair visual perception, causing you to see things that aren’t there or misinterpret what you see.
Heart Disease
Sleep deprivation can lead to chronic cardiovascular problems like hypertension and heart disease. When we sleep our blood pressure drops. Not experiencing this nightly drop in pressure is a major risk factor for heart disease. If you’re sleeping less than 6 hours each night, your risk of heart disease increases by 48%. Also, the likelihood of having a heart attack increases by nearly 100%.
High Blood Pressure
Your heart basically works on overtime when you lack sleep, causing an increase in your blood pressure. If you are getting less than 6 hours of sleep, your risk of developing high blood pressure increases by 20%. If you have hypertension, a single night without adequate sleep can elevate your blood pressure for a whole day. This can potentially increase and lead to other heart conditions.
Immune System
Sleep is vital for your immune system as it’s your body’s time to rest, repair, and fight off any virus or bacteria. Receiving inadequate sleep each night negatively impacts your immune system and reduces its response time. This weakens your defenses against infections, colds, and the flu leaving you more prone to catch something. Those who receive less than 7 hours of sleep are three times more likely to develop a cold or virus.
Injury
You may notice you are more accident prone when you are sleepy. Lack of sleep can make you groggy and affect your balance and coordination, making you more prone to injury due to an accident.
Memory loss
Without the proper amount of sleep, your ability to remember even the smallest things becomes tough. Sleep deprivation can cause your memory for recent happenings to suffer, and even long-term memories may become difficult to access. You need a good night sleep in order for your brain to process and store your memories. The more sleep you lose, the bigger the problem your memory becomes.
Microsleep
If you are severely sleep deprived, you might fall asleep for short periods without even knowing it. That can be very dangerous if you’re behind the wheel of a car.
Moodiness
Sleep deprivation can make you moody, emotional, and quick to anger. From the moment you wake up after a poor night sleep, you may immediately be in a bad mood.
Obesity
Numerous studies have linked chronic sleep loss to obesity. In fact, sleeping less than 6 hours each night can increase your risk of obesity by 30%. Sleep helps maintain the healthy balance of hormones that your body needs to tell you when you’re hungry or full. Lack of sleep disturbs the balance of those hormones causing your brain not to get the message that you’ve had enough to eat and increases your appetite. Also, if you are constantly sleep deprived, you are less likely to have the energy to exercise and take care of your body.
Interesting Fact: You could lose 14.3lbs per year if you sleep for 1 extra hour each day rather than watching TV.
Skin
We’ve all heard the term beauty sleep. Well, it turns out it exists! Research shows that those who do not get enough sleep or have trouble sleeping have increased signs of skin aging. The human growth hormone from the pituitary gland is released while we sleep and is necessary to maintain healthy skin.
Sleep Paralysis
Sleep paralysis is when you are unable to move your body when falling asleep or waking up. If you are sleep deprived, you are more likely to wake in an immobilized REM state, resulting in feelings of fear and panic.
Stroke
Lack of sleep negatively affects cardiovascular health, increasing the risk of restricting blood flow to the brain. This increases your chance of a stroke. Also, you are four times more likely to be at risk of a stoke if you are sleeping less than 6 hours a night.
Yawning
We all yawn, and it is quite normal. However, if you are excessively yawning, it may be because you’re sleep deprived.
How much sleep are you getting? If you feel like it’s not enough, and you’re not sure why – find out by taking our online Sleep Assessment and schedule an appointment with your personal physician to receive a home sleep test from Vitalistics.